Business Process Analysis: A Step-by-Step Approach

Organizations constantly strive to improve efficiency and effectiveness. One way they are achieving this is through business process analysis . This emerging field combines data analysis and process improvement methodologies to provide valuable insights into organizational processes.
By collecting and analyzing data from various sources, such as customer interactions, employee productivity, and resource utilization, businesses can identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas for improvement. This article will explore the importance of business process analysis and how organizations can leverage this powerful tool to stay ahead in today's competitive market.
What is Business Process Analysis?
Business process analysis, called BPA, is a systematic approach to examining and evaluating an organization's business processes. It involves identifying, documenting, and analyzing the current processes to identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas for improvement.
Critical aspects of Business Process Analysis include:
Initiation
In this initial phase, the need for process analysis is identified. This could stem from process inefficiencies, customer complaints, changing business goals, or other factors. The scope and objectives of the analysis are defined, along with the selection of processes to be analyzed.
Planning
A detailed plan is developed to guide the analysis process. This plan includes defining the methodology, tools, resources, timeline, and responsibilities for each stage of the BPA lifecycle.
Data Collection
Relevant data is gathered about the selected process. This can include process documentation, performance metrics, historical data, and stakeholder feedback.
Process Mapping
The current process is mapped out visually using flowcharts, process maps, or other diagramming techniques. This helps understand the sequence of activities, decision points, and interactions.
Data Analysis
Collected data is analyzed to identify patterns, trends, bottlenecks, and inefficiencies. This step often involves applying techniques such as root cause analysis, Pareto analysis, and statistical analysis.
Identifying Improvement Opportunities
Based on the analysis, areas for improvement are identified. These could include specific tasks, interactions, or elements of the process that need modification or automation to enhance efficiency and effectiveness.
Solution Generation
Potential solutions to address the identified issues are brainstormed. Cross-functional teams collaborate to develop creative and feasible solutions that align with the organization's goals.
Future State Design
The chosen solutions are incorporated into a redesigned "future state" process. This new process is designed to mitigate the identified issues and capitalize on the improvement opportunities.
Implementation Planning
A detailed plan is created for implementing the changes to the process. This plan outlines the steps, resources, timeline, and responsibilities required to execute the process improvements.
Testing and Validation
Before full-scale implementation, the proposed changes are tested on a smaller scale or in a controlled environment. This helps identify any potential issues and refine the process further.
Implementation
The approved changes are rolled out across the organization. Stakeholders are informed, trained, and provided with the necessary resources to adapt to the new process.
Monitoring and Evaluation
The implemented changes are closely monitored using KPIs. The performance of the new process is compared to the baseline data to assess the improvements achieved.
Feedback Collection
Employees, stakeholders, and customers receive feedback from the process. This feedback is valuable for making ongoing adjustments and refinements.
Continuous Improvement
The BPA lifecycle is a continuous process. The process is continually monitored, analyzed, and refined based on feedback, new data, and changing business requirements to ensure ongoing optimization.
Documentation and Communication
Throughout the BPA lifecycle, documentation is maintained to capture the analysis process, findings, changes made, and their impact. This documentation aids in knowledge sharing and future reference.
Business process analysis (BPA) vs. business analysis
Business Process Analysis (BPA) and Business Analysis are essential practices that contribute to organizational improvement but focus on different aspects of an organization's operations. Here's a comparison between the two:
A. Business Process Analysis, BPA is a specific subset of business analysis that concentrates on evaluating and optimizing the processes within an organization. BPA aims to improve these processes' efficiency, effectiveness, and performance. It involves analyzing how tasks and activities are executed, identifying bottlenecks, and suggesting changes to enhance workflow. BPA is process-centric and often involves visualizing processes using flowcharts, process maps, and diagrams. Its primary focus is on improving operational efficiency and reducing waste.
B. Business Analysis encompasses a broader range of activities that involve identifying business needs, opportunities, and problems and proposing solutions. Business analysts analyze various aspects of an organization, including processes, systems, strategies, and structures. Their goal is to understand the overall business context, gather requirements for projects or initiatives, and facilitate effective communication between stakeholders. Business analysis may involve conducting feasibility studies, defining business requirements, facilitating change management, and ensuring alignment between business goals and technology solutions.
Keys differences between BPA and BA

1. Scope:
- BPA focuses explicitly on evaluating and improving processes within an organization.
- Business analysis has a broader scope, encompassing various aspects of the business, such as strategy, requirements, and technology.
2. Focus:
- BPA emphasizes process efficiency, optimization, and elimination of bottlenecks.
- Business analysis focuses on understanding business needs, solving problems, and facilitating change.
3. Tools and Techniques:
- BPA often uses process mapping, flowcharts, simulations, and data analysis techniques to optimize processes.
- Business analysis employs requirements gathering, stakeholder interviews, SWOT analysis, and cost-benefit analysis.
4. Outcome:
- The primary outcome of BPA is a streamlined and more efficient process flow.
- Business analysis results in a comprehensive understanding of business needs, potential solutions, and actionable recommendations.
5. Stakeholders:
- BPA involves stakeholders primarily concerned with the efficiency and effectiveness of specific processes.
- Business analysis engages various stakeholders, including executives, users, IT teams, and external partners.
6. Role:
- BPA specialists specifically focus on process improvement and optimization.
- Business analysts play a broader role, translating business needs into actionable plans, facilitating communication, and ensuring alignment between different functions.
Business Process Management in Business Process Analysis
When discussing "Business Process Management" within the practice of "Business Process Analysis," it refers to integrating the principles and practices of BPM into analyzing business processes. This means considering how BPM principles can enhance the analysis process, leading to more effective and impactful results.
Key Aspects of Business Process Management in Business Process Analysis:
- Strategic Alignment: Ensuring that the analysis process is aligned with the overall business strategy and goals to drive meaningful improvements.
- Process Design: Using BPM principles to design an efficient, structured analysis process that follows best practices.
- Process Execution: Applying BPM practices to execute the analysis process consistently and efficiently across different processes within the organization.
- Monitoring and Metrics: Incorporating BPM metrics to measure the effectiveness of the analysis process and track key performance indicators.
- Continuous Improvement: Infusing BPM's philosophy of continuous improvement into the analysis process, making it a cycle of ongoing enhancement.
- Change Management: Using BPM's change management techniques to facilitate the adoption of recommended improvements resulting from the analysis.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration: Applying BPM's emphasis on cross-functional collaboration ensures that various stakeholders contribute their insights during the analysis.
- Technology Integration: Leveraging BPM tools and technology to streamline data collection, analysis, and documentation.
- Standardization: Implementing BPM's approach to standardizing processes, ensuring consistency in how analyses are conducted across the organization.
How to Perform a Business Process Analysis?
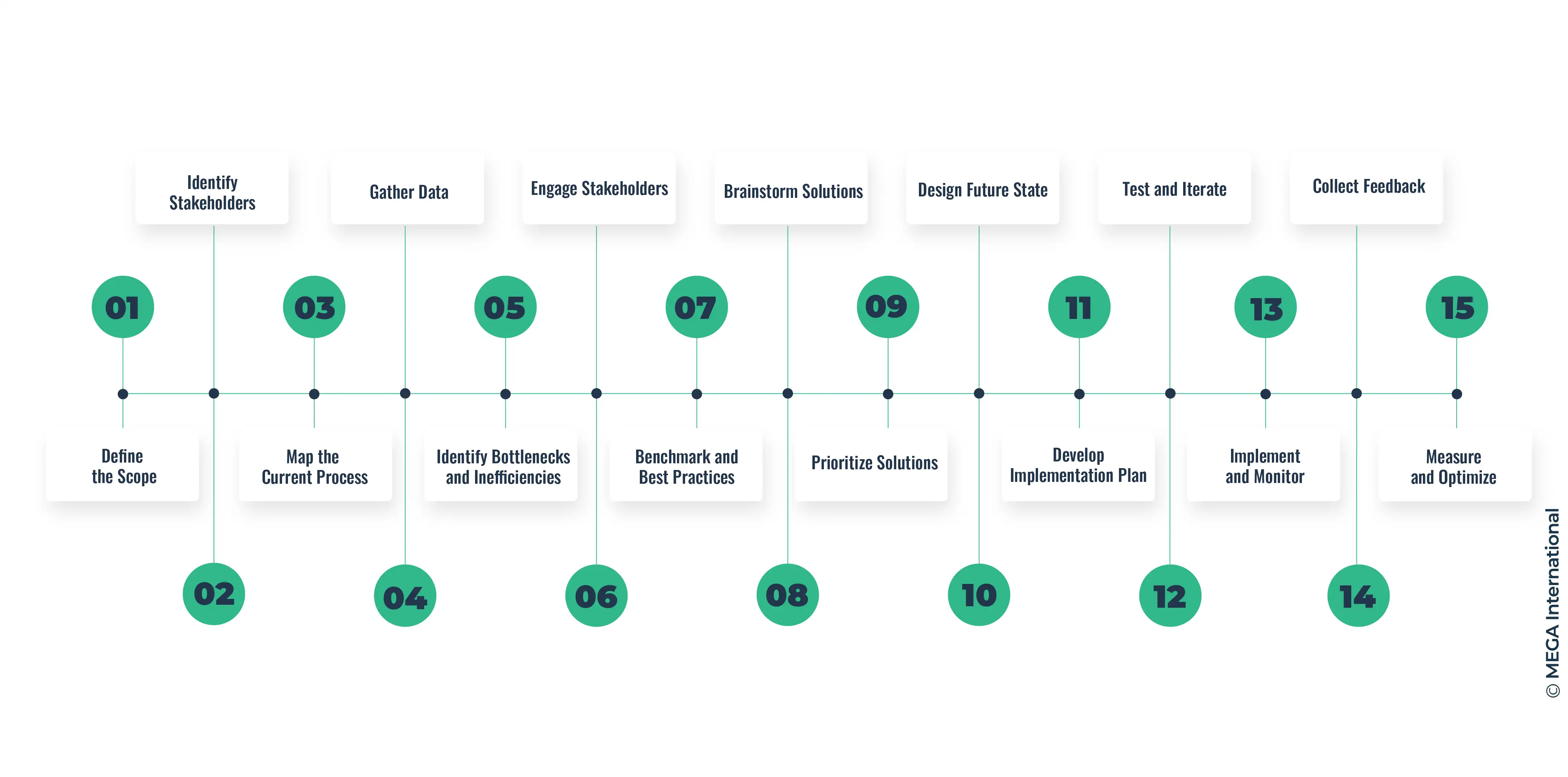
Steps involved in performing a BPA
Performing a Business Process Analysis involves thoroughly examining and understanding the processes within a business to identify inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and areas for improvement. Here's a step-by-step guide to conducting a BPA:
- Define the Scope: Clearly define the scope of your analysis. Identify the specific process or processes you want to analyze. This will help you stay focused and ensure that your analysis is comprehensive.
- Identify Stakeholders: Determine who is involved in or affected by the process. This includes employees, customers, suppliers, and any other relevant parties. Understanding their perspectives will provide valuable insights.
- Map the Current Process: Create a visual representation of the current process using flowcharts, diagrams, or process maps. This should outline each process step, the sequence of activities, decision points, inputs, outputs, and the people or departments involved at each stage.
- Gather Data: Collect data related to the process, such as time taken at each step, resource utilization, error rates, and other relevant metrics. This data will help you identify areas of improvement.
- Identify Bottlenecks and Inefficiencies: Analyze the process map and data to identify bottlenecks, redundancies, delays, and inefficiencies. Look for steps that take longer than necessary or contribute to errors.
- Engage Stakeholders: Discuss the process with stakeholders to gain their insights and feedback. They might offer unique perspectives on pain points and possible improvements.
- Benchmark and Best Practices: Research industry benchmarks and practices related to the process. Compare your findings to these benchmarks to identify gaps and areas for improvement.
- Brainstorm Solutions: Collaborate with a cross-functional team to brainstorm potential solutions to the identified issues. Encourage creative thinking and consider both short-term and long-term solutions.
- Prioritize Solutions: Not all issues will have the same impact. Prioritize solutions based on their potential impact, feasibility, and alignment with business goals.
- Design Future State: Design a new and improved process flow based on the prioritized solutions. This should address the identified issues and incorporate the best practices and innovative ideas.
- Develop Implementation Plan: Create a detailed plan for implementing the proposed changes. This plan should outline the necessary resources, timeline, responsibilities, and potential challenges.
- Test and Iterate: Before fully implementing the changes, consider conducting a pilot test on a small scale. This allows you to identify any unforeseen issues and refine the process further.
- Implement and Monitor: Roll out the new process based on the finalized implementation plan. Monitor its performance closely to ensure that the anticipated improvements are being realized.
- Collect Feedback: Continuously collect feedback from stakeholders involved in the new process. This feedback will help you make further adjustments and refinements.
- Measure and Optimize: Track KPIs to measure the success of the new process. Make data-driven adjustments as needed to optimize the process over time continually.
Business Process Analysis is an iterative process. As your business evolves and changes, processes may need to be reanalyzed and refined to remain efficient and effective .
Effective business process analysis methods
Here are some practical business analysis methods that can help you thoroughly assess and improve your business processes:
- Flowcharts and Process Maps: Visualize the workflow of your process using flowcharts or process maps. These visual representations help identify the activity sequence, decision points, and interactions between different steps.
- Value Stream Mapping: This method identifies the value-added and non-value-added activities within a process. It helps understand the flow of materials, information, and activities from start to finish.
- Customer Journey Mapping: Focus on the customer's perspective by mapping out the customer's journey when interacting with your business. This helps in identifying pain points and opportunities for enhancement.
- Process Simulation: Use software tools to create simulations of your processes. This allows you to test different scenarios and variations, helping you identify the impact of changes before implementing them.
- Process Mining: Utilize specialized software to analyze digital traces left by processes in your information systems. This data-driven method provides insights into the actual execution of processes.
- SWOT Analysis: Conduct a SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) analysis for your process. This helps you identify internal strengths and weaknesses and external opportunities and threats that may impact the process.
- Root Cause Analysis: When encountering issues or inefficiencies, use techniques like the "5 Whys" to dig deep and identify the root causes behind these problems. This method helps in addressing underlying issues rather than just addressing symptoms.
- Benchmarking: Compare your processes with those of industry leaders or competitors. This helps you identify best practices and areas where your processes can be improved to match or exceed industry standards.
- Interviews and Surveys: Gather insights from employees, stakeholders, and customers through interviews and surveys. Their firsthand experiences can provide valuable information about pain points and potential improvements.
- Pareto Analysis: Focus on the most significant issues by applying the 80/20 rule. Identify the 20% of process elements causing 80% of the problems and prioritize improvements accordingly.
- Kaizen (Continuous Improvement): Adopt a philosophy of continuous improvement where small changes are consistently made to improve processes over time. Encourage employees to contribute ideas for improvement.
- Fishbone Diagram (Ishikawa or Cause-and-Effect Diagram): Use this diagram to visualize the various factors contributing to a problem. Categories such as people, processes, equipment, materials, and environment are used to identify potential causes.
- Critical Path Analysis: Particularly useful for project-based processes, critical path analysis identifies the sequence of tasks that must be completed on time to ensure the overall process meets its deadlines.
- Gantt Charts: Display the timeline and dependencies of various tasks in your process using Gantt charts. This helps in understanding the sequence and duration of activities.
- Six Sigma: Incorporate Six Sigma methodologies to reduce process defects and variations. Techniques like DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) can be applied.
- Select the methods that align with your goals, resources and the complexity of your analyzing processes.
Tools and techniques for conducting a business process analysis
Several tools and techniques can aid in the analysis of business processes. Business process analysis tools help document and visualize processes, track performance metrics, and identify areas for improvement.
These tools include process modeling software, analytics platforms, and workflow management systems. Additionally, engaging with subject matter experts and conducting interviews and surveys can provide valuable insights for the analysis.
How to Implement Business Process Analysis Methods?
Implementing Performing business process analysis methods involves systematically applying techniques and tools to improve your business processes. Here's a step-by-step guide to help you effectively implement these methods:
- Identify Goals and Objectives: Clearly define what you want to achieve through the business process analysis. Whether it's reducing inefficiencies, improving customer satisfaction, or optimizing resource utilization, having clear goals will guide your analysis efforts.
- Select Appropriate Methods: Choose the methods and tools that align with your goals and the complexity of your analyzing processes. Consider resources, data availability, and your team's expertise.
- Assemble a Cross-Functional Team: Form a team that includes representatives from different departments or areas relevant to the process. This diversity ensures that various perspectives are considered during the analysis.
- Map the Current Process: Begin by visualizing the current process using flowcharts, process maps, or value stream maps. This helps in understanding the existing workflow and identifying potential areas for improvement.
- Gather Data: Collect relevant data related to the process. This can include cycle times, error rates, resource utilization, and customer feedback. Accurate data is crucial for making informed decisions.
- Analyze the Data: Use the selected analysis methods, such as Pareto analysis, root cause analysis, or SWOT analysis, to delve into the data and identify patterns, trends, and areas of concern.
- Identify Improvement Opportunities: Based on the analysis, pinpoint areas where improvements are needed. Prioritize these opportunities based on their potential impact and feasibility.
- Brainstorm Solutions: Engage your cross-functional team in brainstorming sessions to generate potential solutions for the identified issues. Encourage creative thinking and consider both incremental and transformative changes.
- Design the Future State: Develop a new and improved process flow based on the brainstormed solutions. This should address the identified issues and incorporate best practices.
- Test and Validate: Before implementing changes on a larger scale, consider conducting pilot tests. Implement the new process in a controlled environment to identify any unforeseen challenges.
- Create an Implementation Plan: Develop a detailed plan that outlines the steps, resources, timeline, and responsibilities for implementing the new process. Consider potential risks and mitigation strategies.
- Communicate and Train: Communicate the upcoming changes to all stakeholders and provide necessary training to ensure a smooth transition to the new process. Address any concerns or questions they may have.
- Implement Changes: Roll out the changes based on the implementation plan. Monitor the process closely during the transition phase and be prepared to adjust if needed.
- Monitor and Measure: Continuously monitor the performance of the new process using key performance indicators (KPIs). Compare these metrics to the baseline data to assess the improvements achieved.
- Collect Feedback and Iterate: Gather feedback from employees, stakeholders, and customers interacting with the new process. Use their insights to fine-tune and optimize the process further.
- Document the Changes: Maintain comprehensive documentation of the changes made, their rationale, and their impact on performance. This documentation will be valuable for future reference.
- Celebrate Success and Learn: Acknowledge and celebrate the successes achieved through process analysis and improvement efforts. Also, identify lessons learned to apply to future analysis projects.
Remember that BPA is an ongoing process. Regularly revisit the improved process to ensure it remains effective and aligned with evolving business needs.
Importance of Automation in today's business landscape
Automation and Business Process Analysis (BPA) are closely related concepts that work together to improve organizational efficiency and effectiveness. Here's how automation and BPA intersect and complement each other.
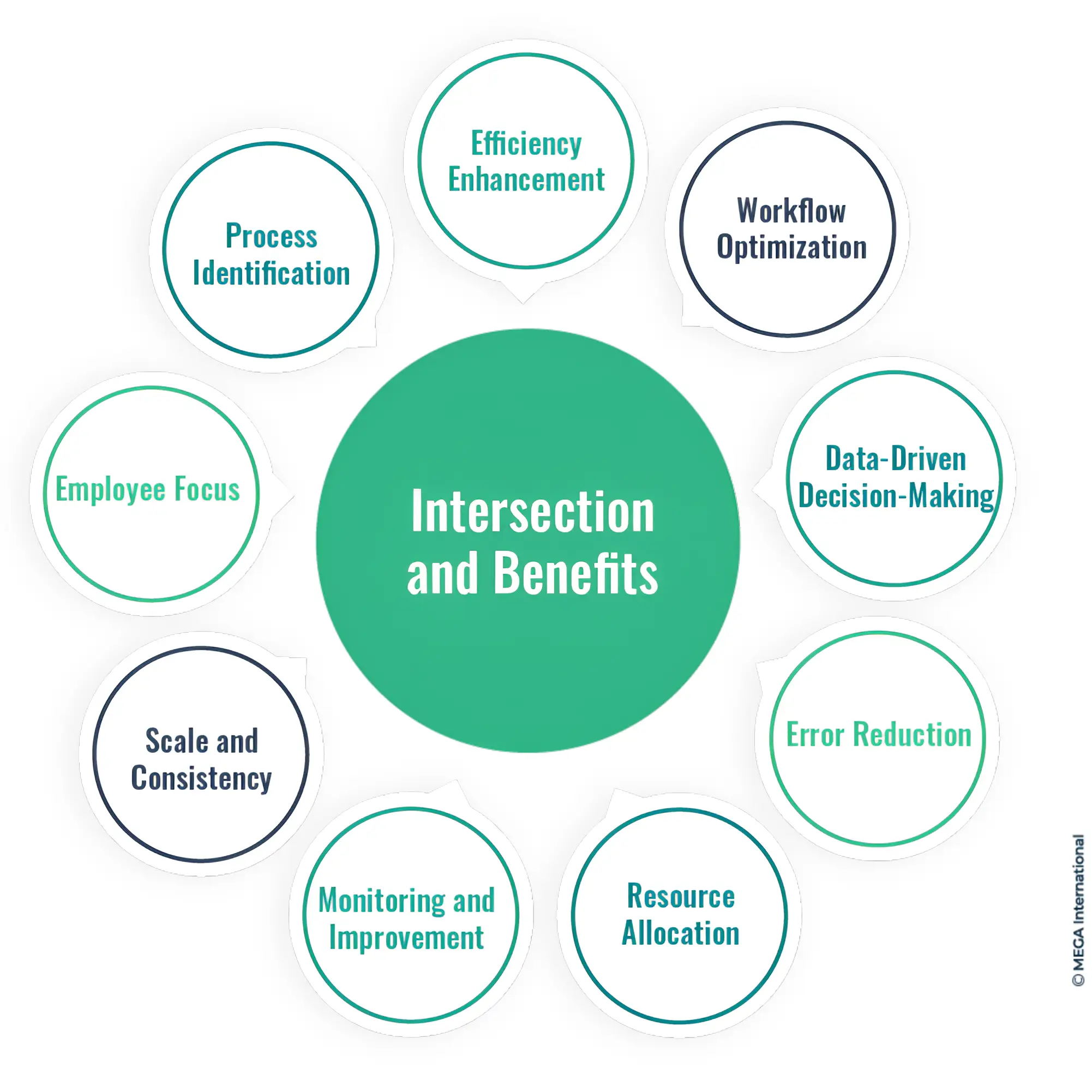
Intersection and Benefits:
- Process Identification: BPA identifies processes that are candidates for automation. By analyzing processes, BPA helps determine which tasks can be automated for greater efficiency.
- Efficiency Enhancement: BPA uncovers inefficiencies within processes. Automation targets these inefficiencies by automating repetitive, time-consuming, and error-prone tasks, leading to improved efficiency.
- Workflow Optimization: Automation enhances process flows identified during BPA. Automating tasks can optimize the sequence of activities for smoother execution.
- Data-Driven Decision-Making: BPA provides data-driven insights into process performance. Automation leverages this data to decide which tasks are best suited for automation.
- Error Reduction: Automation reduces the risk of errors by eliminating manual data entry and repetitive tasks identified during BPA.
- Resource Allocation: BPA identifies resource bottlenecks. Automation optimizes resource allocation by ensuring resources are utilized efficiently.
- Monitoring and Improvement: Automation provides real-time data on process execution. BPA can analyze this data to identify further opportunities for improvement.
- Scale and Consistency: Automation ensures consistent execution of tasks across the organization, which aligns with the standardization goals of BPA.
- Employee Focus: Automating routine tasks frees employees to focus on more strategic and value-added activities, aligning with BPA's goal of process improvement.
Challenges:
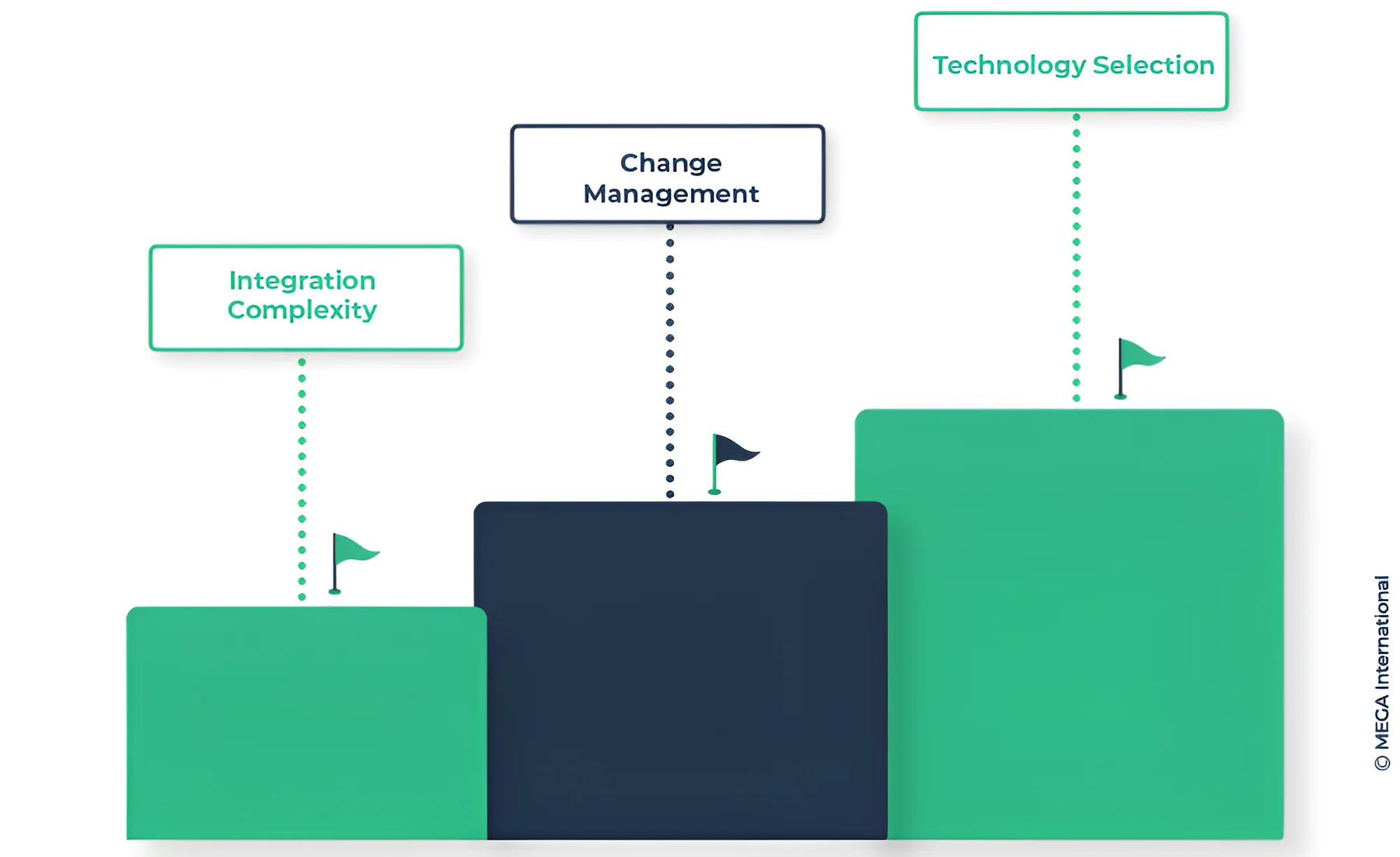
- Integration Complexity: Integrating automation solutions into existing processes can be complex and require careful planning to ensure smooth implementation.
- Change Management: Employees may resist automation due to fear of job displacement. Proper change management, as part of BPA, can address these concerns.
- Technology Selection: Selecting the right automation tools and technologies requires considering the specific needs of the processes identified during BPA.
Benefits of Business Process Analysis
Business Process Analysis (BPA) offers a range of significant benefits to organizations looking to enhance their operations, efficiency, and overall performance. Here are some critical advantages of conducting Business Process Analysis:
- Alignment with Strategic Goals: BPA helps ensure that processes are aligned with the company's strategic objectives. It facilitates measuring process performance against these goals and allows adjustments as needed.
- Efficiency Improvement: BPA helps identify business process bottlenecks, redundancies, and inefficiencies. By streamlining these processes, companies can reduce operational costs and optimize resource allocation.
- Increased Productivity: Streamlining processes and eliminating bottlenecks can lead to increased productivity. Employees can focus on value-added tasks rather than spending time on manual, time-consuming activities.
- Cost Reduction: By eliminating unnecessary steps and automating repetitive tasks, BPA can lead to cost savings, better resource allocation, and reduced waste.
- Compliance and Risk Management: BPA can help ensure that processes comply with regulations and industry standards. It also helps identify and mitigate risks by highlighting potential areas of vulnerability in processes.
- Enhanced Quality: BPA can lead to improved product or service quality. By identifying and addressing process flaws, companies can reduce errors and defects, resulting in higher customer satisfaction.
- Customer Satisfaction: Improved processes often lead to better customer experiences. Timely and error-free delivery of products or services can enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Better Decision-Making: BPA provides valuable data and insights into how processes are performing. This data can be used for informed decision-making, helping companies adapt to changing market conditions more effectively.
- Competitive Advantage: Companies that continuously analyze and improve their processes are better positioned to adapt to market changes and stay ahead of competitors.
- Innovation: BPA can spark innovation by encouraging employees to think creatively about how to improve processes. This can lead to the development of new products, services, or business methods.
Shorter Time-to-Market: Streamlined processes often result in faster product or service development cycles, enabling companies to bring new offerings to market more quickly.
Employee Engagement: Involving employees in the BPA process can boost their engagement and morale. When employees see that their input is valued and their work processes are being improved, it can lead to a more positive work environment.
Challenges
Implementing Business Process Analysis can bring about significant improvements, but it also comes with challenges. Here are some common challenges that organizations may face when conducting BPA:
- Cultural Resistance: Organizational culture may not be conducive to change or process improvement. Shifting the culture to embrace continuous improvement is a gradual process.
- Misaligned Priorities: BPA efforts may not align with the organization's strategic priorities, leading to a lack of support and commitment from management.
- Lack of Stakeholder Buy-In: Without buy-in from critical stakeholders, including top management, the BPA initiatives may lack the necessary support and resources to succeed.
- Data Availability and Quality: Insufficient or poor-quality data can hinder accurate analysis and decision-making.
- Complex Processes: Analyzing and improving complex processes can be challenging due to their intricacies, making it harder to identify root causes and implement effective solutions.
- Limited Resources: Conducting a thorough BPA requires time, expertise, and resources.
- Scope Creep: Expanding the scope of BPA projects beyond their original objectives can lead to inefficiencies and scope creep, delaying results and adding complexity.
- Overemphasis on Technology: While technology can enhance BPA efforts, solely focusing on technology without considering people, processes, and culture can lead to ineffective outcomes.
- Process Ownership and Accountability: Identifying process owners and ensuring accountability for process improvements can be challenging, especially in organizations with complex structures.
- Inadequate Communication: Poor communication about BPA goals, progress, and outcomes can lead to employee confusion and resistance.
- Unrealistic Expectations: Expecting immediate and dramatic improvements from BPA initiatives can lead to disappointment if the results do not meet overly optimistic expectations.
- Lack of Continuous Monitoring: Once changes are implemented, failing to monitor and adjust processes consistently can lead to regression into old habits and inefficiencies.
- External Factors: External factors such as regulation changes, market dynamics, or economic conditions can impact the success of BPA initiatives.






